E0124
INTRAMOLECULAR HYDROGEN BONDING IN SOME AZOENAMINONES. Bernardo Lages Rodrigues and Maria Teresa do Prado Gambardella, Instituto de Química de São Carlos - Universidade de São Paulo - Brazil
Crystal Structures of four azoenaminones (Figure 1) were determinated using X-ray diffraction. Intramolecular hydrogen bonds strengths are correlated to the differences in the aromatic ring and amino nitrogen electron densities produced by the presence of the different substituints. Data clearly show that the stronger the O1-H-N2 hydrogen bond, the weaker the N3-H-N1 resonance assisted hydrogen bond is.
Crystal data: (I): C13H16N4O5, P21/n, a=7.345(1), b=9.937(1), c=19.725(2)(, (=91.440(9)(, V=1419.9(3, Z=4, R(F) = 0.052, wR(F)=0.058; (II): C13H16N3O3Cl, P21/n, a=7.566(2), b=9.823(1), c=19.111(2)(, (=91.35(1)(, V=1439.3(3)(3, Z=4, R(F)=0.047, wR(F)=0.069; (III): C16H21N4O5Cl, P21/c, a=7.324(2), b=22.790(6), c=11.715(2)(, (=106.59(1)(, V=1874.1(7)(3, Z=4, R(F2)=0.053; wR(F2)=0.095; (IV): C12H13N4O5Cl P21/c, a=9.238(2), b=14.388(3), c=11.763(2)(, (=109.40(4)(, V=1474.8(5)(3, Z=4, R(F)=0.045, wR(F)=0.040.
(I): R1=H, R2=NO2, R3=CH3 (II): R1=H, R2=C1, R3=CH3 (III):R1= R2=C1, R3=H NO2, (IV):R1= R2=C1, R3=C(CH3) NO2, 3
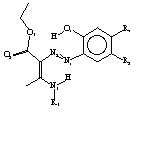
Figure 1-Structures determinated