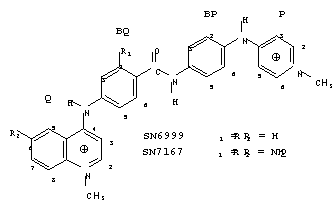
CONFORMATIONAL CHANGES ON GROOVE BINDING TO DNA : MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF SN7167 COMPLEXED WITH d(CGCGAATTCGCG)2. Christopher J. Squire+, George R. Clark+, William A. Denny[[daggerdbl]], +Chemistry Department, [[daggerdbl]]Cancer Research Laboratory, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand.

The X-ray crystal structure of the synthetic antitumour and antiviral minor groove binding drug SN7167 and the DNA oligonucleotide d(CGCGAATTCGCG)2
has been determined to an R factor of 20.0% at 2.6 Å resolution. The SN7167 molecule binds in the minor groove over the AATTCG sequence with the methylpyridinium (P) ring near to the G10-C15 base pair and the bulky methylquinolinium (Q) extending as far as the A5-T20 base pair. The drug binds weakly to the DNA as evidenced by long-range contacts and shallow penetration into the groove. We are in the process of analysing the nature of these weak interactions. This structure will be compared with that of the complex between the parent drug SN6999 and the alkylated DNA d(CGC[e6G]AATTCGCG)2 [Y. Gao, M. Sriram, W. A. Denny, A. H.-J. Wang, (1993). Biochemistry, 32, 9639-9648]. There are significant differences between the two structures in the extent of DNA bending, drug conformation and groove binding.