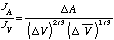 ,
,
CORRELATION BETWEEN SURFACE AND VOLUME: A METHOD OF THE CRYSTAL HABlTUS DESCRIPTION A. M. Ivanov and Yu. M. Smirnov Tver State University, 170000 Tver, Russia
The habitus and morphology of crystals are subject to considerable changes by the melt supercooling. In [1] we described a method enabling the analysis of the volume and surface changes during the crystal growth. The method is based on the comparison of the flux densities of extensive quantities. These quantities are presented by surface (area) A and volume V.
The main equation is
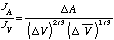 ,
,
where JA, JV are the flux densities, [[Delta]]A, [[Delta]]V are the changes of A and V at the interval of time, and [[Delta]]V is the averaged volume of the crystal.
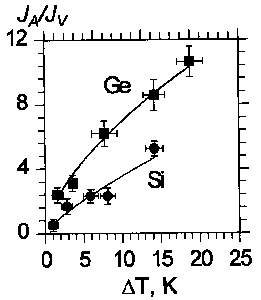
Shown in the figure is the dependence of the defined parameter on the melt supercooling [[Delta]]T for germanium (Ge) and silicon (Si). The JA/JV increases with supercooling and morphology in the following order: antiskeleton - face form - skeleton - dendrite.
This method was applied to the study of ceramics [2] prepared from natural raw materials. The samples were interpreted as conglomerates composed of "skeleton" and "filler"phases. Following this approach the variation of the phase ratio was determined as a function of the firing regimes and concentration of the fusing agents. The dependences obtained appear to have a good correlation with the mechanical properties of ceramics.
The results of the present study indicate that the method employed is of advantage for both single crystals and polycrystalline materials.
[1] Yu. M. Smirnov and G. S. Blokhina. Melt supercooling and crystal morphology. In: Physics of Crystallization (Kalinin, KSU, 1983), p. 13.
[2] Yu. M. Smirnov and A. M. Ivanov. Classification of clay additives. In: Physics of Crystallization (Tver, TSU, 1994), p. 86.