A STUDY OF MONO- AND BISLACTONE RING FORMATION OF DEOXYCHOLIC ACID AND ITS NOR AND HOMO DERIVATIVES. S.Stankovic, D.Lazar, K.Kuhajda and D.Miljkovic Faculty of Sciences, University of Novi Sad, Trg Dositeja Obradovica 4, 21000 Novi Sad, Serbia, Yugoslavia
The formation of 3[[alpha]]-acetoxy-5,[[beta]]-cholano-bislactone (from 3-O-acetyl deoxycholic acid) was described in our earlier paper (1). In order to study further the lactonization processes in similar compounds, we have examined the chemical and structural features of 24-nor-5[[beta]]-cholan-23-oic acid. The structure was determined by X-ray diffraction. Contrary to our earlier finding, in this case the monolactonization process occured exclusively.
The pairs of molecules with 7-membered monolactone rings are related by a pseudo twofold axis, resembling molecules with 16-membered bislactone rings which possess the same element of symmetry.
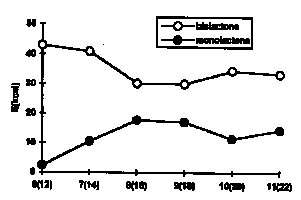
Energetical examinations, applied to similar molecules containing 6- to 11-membered monolactone and 12- to 22- membered bislactone rings (obtained by modeling),are summarized in graphs. The relative energy minimum values, obtained by MMX calculations, show a dramatic change between molecules with 7- and 8- membered monolactone and, consequently 14- and 16- membered bislactone rings, which is in full agreement with our experimental results.
Conformational examinations show that the carbonyl oxygens from lactone moiety change their orientations from [[alpha]]- to [[beta]]-face between 14 and 16-membered bislactone rings.
(1) S.Stankovic et al., J.Mol.Struc.,221 (1990), 271.
