DIRECT OBSERVATION OF HYDROGEN - DEUTERIUM EXCHANGE IN COBALOXIME CRYSTALS BY NEUTRON DIFFRACTION. Y. Ohgoa , Y. Ohashia, W. T. Kloosterb and T. F. Koetzleb , aDepartment of Chemistry, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 152, Japan, bChemistry Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, New York 11973-5000
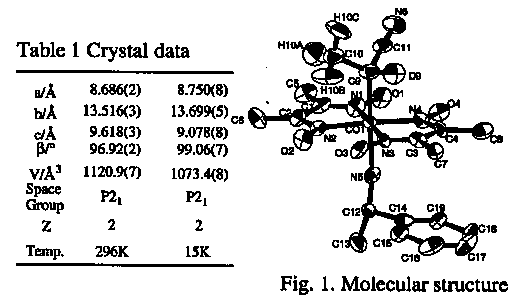
It has been found that the chiral alkyl groups bonded to the cobalt atom in some cobaloxime complexes are racemized on exposure to visible light in the solid-state. To examine the mechanism of crystalline-state racemization we prepared cobaloxime complexes which have deuterium instead of hydrogen bonded to the chiral carbon of the cyanoethyl group and analyzed the crystal structure before and after the photoirradiation by neutron diffraction. The molecular structure before irradiation is shown in Fig. 1.
The structure after irradiation showed that the deuterium, D9, was exchanged with one of hydrogen atom of the neighboring methyl group, H10B. This may suggest quite a new mechanism of the racemization.
