STRUCTURAL VARIATIONS OF SODIUM PHENOLATE WITH DIFFERENT DONOR LIGANDS. J. Sielera), M. Kunertb), E. Dinjusb), a)Institut für Anorganische Chemie der Universität, D-04103 Leipzig, Linnestr. 3, b)Max-Planck-Gruppe für CO2-Chemie, D-07743 Jena, August-Bebel-Str.2
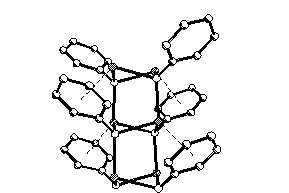
Even though sodium phenolate has been applied industrially (Kolbe-Schmitt synthesis) since 1874, its crystal structure was still unknown. Recently, we succeeded in growing single crystals of solvent-free NaOPh, using a Bridgeman- Stockbarger-apparate. In the solid state, NaOPh forms polymeric one-dimensionals chains of dimeric units (Na2O2 rings), arranged along [001]. The coordination number of each Na atom is three. Remarkably, the Na atom also interacts with the neighboring phenyl ring (Na - C1 2.81(1) Na - C2 2.79(1)Å).
Sodium phenolate reacts with ethers (thf, 1,2-dimethoxyethane(dme)) with formation of tetrameric [Na(dme)OPh]4 or hexameric [Na(thf )OPh]6 units.
We believe that these studies will help to unterstand the reactivity of NaOPh towards CO2 in the Kolbe-Schmitt synthesis.

Figure 1 : Solid state structure of NaOPh