SELECTIVE INCLUSION OF KETONE BY A SEXIPEDAL HOST.
Katherine L. Gifford Nasha, Susan A. Bournea, Fumio Todab. a) Department of Chemistry, University of Cape Town, Rondebosch, 7700, South Africa. b) Department of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering, Ehime University, Matsuyama 790, Japan.
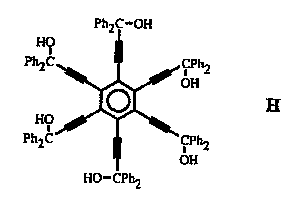
Hexakis(3-hydroxy-3,3-diphenyl-2-propenyl)benzene (H) has proved to be a very versatile host including a number of small organic molecules via hydrogen bonding. Inclusion compounds of H have been found to form in various host:guest ratios, often considerably richer in guest than is usually observed for organic hosts. It includes a number of guests with carbonyl functions, for example methyl ethyl ketone (1:3), diethyl ketone (1:2) and cyclohexanone (1:5); as well as guests such as diethyl ether (1:2) and 1,4-dioxane (1:5).
However, on crystallization from 1,3-dioxolane, H selectively included a trace amount of 1,3-dioxolan-2-one from the solution. This ketone complex was characterised by single crystal diffraction, thermal analysis, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and mass spectroscopy.
