STRUCTURE OF A LEAD COMPLEX USED IN FOOD ANALYSIS. M. Rossi. M-L. Chan, Department of Chemistry, Vassar College, Poughkeepsie, NY 12601 and F. Caruso, Istituto di Strutturistica Chimica, CNR, 00016 Monterotondo Stazione (Rome), Italy.
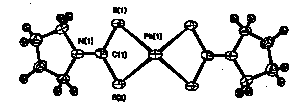
A method for determining the lead content in foods is by chelating lead with ammonium pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate. Crystal structure analysis of this lead complex shows an orthorhombic cell, Pccn, with Z=4, a = 13.839(14)Å, b = 14.058(16)Å, c = 7.763(6)Å. The structure is shown below.
The Pb---Pb intermolecular distance is 3.881(6)Å and the molecules stack along the c axis. Along the stacking direction, there are weak intermolecular interactions among the successive molecules and the Pb---S distances are 3.477(6)Å for Pb-S1 and 3.283(5)Å for Pb-S2. The results of this structure analysis will be contrasted to similar compounds.
